Collaborators: Abdou Padane, Houriiyah Tegally, Yajna Ramphal, Ndiaye Seyni, Mariéma Sarr, Mame Matar Diop, Cyrille Kouligueul Diedhiou, Aminata Mboup, Ndèye Dieyna Diouf, Abdoulaye Souaré, Ndéye Diabou Diagne, Marilyne Aza-Gnandji, Ndèye Astou Dabo, Yacine Amet Dia, Ndeye Aminata Diaw, Nafissatou Leye, Papa Alassane Diaw, Ambroise Ahouidi, Badara Cissé, Abdoulaye Samba Diallo, Ousmane Diop, Abdou Aziz Diallo, Souadou Ndoye, Tomasz J. Sanko, Cheryl Baxter, Eduan Wilkinson, James E. San, Derek Tshabuila, Yeshnee Naidoo, Sureshnee Pillay, Richard Lessells, Khady Cissé, Abdoulaye Leye, Khalifa Ababacar Mbaye, Dramane Kania, Bachirou Tinto, Isidore Traoré, Sampawendé Thérèse Kagone, Abdoul Salam Ouedraogo, Robert J. Gifford, José Lourenço, Marta Giovanetti, Jennifer Giandhari, Tulio de Oliveira, Souleymane Mboup
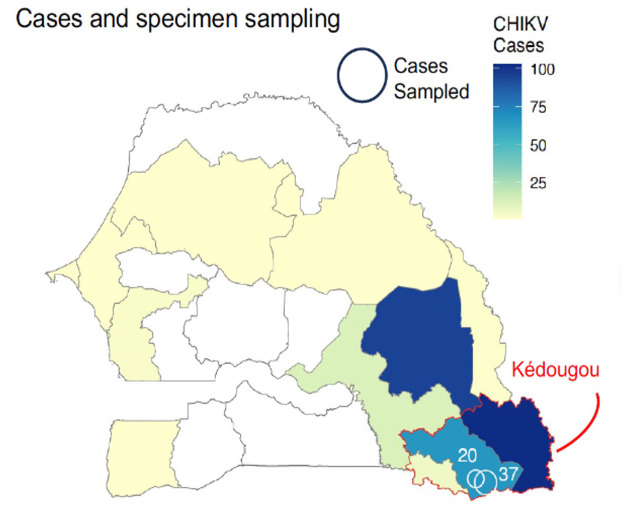
Summary: AbstractChikungunya (CHIKV) is a re-emerging endemic arbovirus in West Africa. Since July 2023, Senegal and Burkina Faso have been experiencing an ongoing outbreak, with over 300 confirmed cases detected so far in the regions of Kédougou and Tambacounda in Senegal, the largest recorded outbreak yet. CHIKV is typically maintained in a sylvatic cycle in Senegal but its evolution and factors contributing to re-emergence are so far unknown in West Africa, leaving a gap in understanding and responding to recurrent epidemics. We produced, in real-time, the first locally-generated and publicly available CHIKV whole genomes in West Africa, to characterize the genetic diversity of circulating strains, along with phylodynamic analysis to estimate time of emergence and population growth dynamics. A novel strain of the West African genotype, phylogenetically distinct from strains circulating in previous outbreaks, was identified. This suggests a likely new spillover from sylvatic cycles in rural Senegal and potential of seeding larger epidemics in urban settings in Senegal and elsewhere.
Publication Date: 2023-11-15
Journal: medRxiv
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.14.23298527