Collaborators: Adugna Abera, Houriiyah Tegally, Geremew Tasew, Eduan Wilkinson, Abraham Ali, Feyisa Regasa, Molalegne Bitew, Lucious Chabuka, Gaspary Mwanyika, Derek Tshiabuila, Jennifer Giandhari, Sureshnee Pillay, Jenicca Poogavanan, Monika Moir, Moritz U.G. Kraemer, Kamran Khan, Carmen Huber, Getachew Tollera, Tobias F. Rinke de Wit, Cheryl Baxter, Richard Lessells, Dawit Wolday, Dereje Beyene, Tulio de Oliveira,
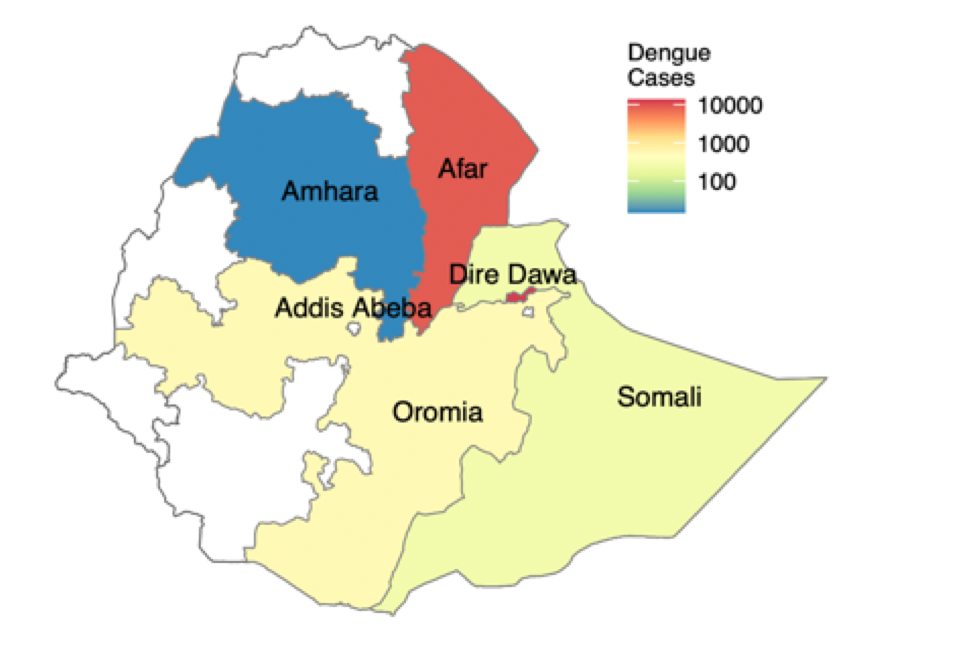
Summary: ABSTRACTIn Ethiopia, dengue virus (DENV) infections have been reported in several regions, however, little is known about the circulating genetic diversity. Here, we conducted clinical surveillance for DENV during the 2023 nationwide outbreak and sequenced DENV whole genomes for the first time in Ethiopia. We enrolled patients at three sentinel hospital sites. Using RT-PCR, we screened serum samples for three arboviruses followed by serotyping and sequencing for DENV-positive samples (10.4% of samples). We detected two DENV serotypes (DENV1 and DENV3). Phylogenetic analysis identified one transmission cluster of DENV1 (genotype III major lineage A), and two clusters of DENV3 (genotype III major lineage B). The first showed close evolutionary relationship to the 2023 Italian outbreak and the second cluster to Indian isolates. Co-circulation of DENV1 and DENV3 in some regions of Ethiopia highlights the potential for severe dengue. Intensified surveillance and coordinated public health response are needed to address the threat of severe dengue outbreaks.
Publication Date: 2024-07-10
Journal: medRxiv
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.10.24310195